Streamlining Databricks Deployments with Databricks Asset Bundles (DABs) and GitLab CI/CD
March 21st, 2025 WRITTEN BY FGadmin

Written by Atharva Shrivas, Consultant, Data Management and Ashutosh Yesekar, Consultant, Data Management
As data engineering and analytics pipelines become more complex, organizations need efficient ways to manage deployments and enhance collaboration. Traditional approaches often involve redundant code, scattered dependencies, and inconsistent environments.
Databricks Asset Bundles (DABs) provide a structured, streamlined way to package, share, and deploy Databricks assets, simplifying collaboration across teams and environments. By integrating GitLab CI/CD, we can automate the entire development lifecycle, ensuring efficient version control, validation, and controlled deployments across multiple Databricks workspaces.
In this blog, we’ll explore how DABs can enhance data projects and streamline workflows, empowering organizations to navigate the complexities of modern data engineering effectively.
Who Can Leverage DABs?
DABs are particularly useful in scenarios where:
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is required for managing Databricks jobs, notebooks, and dependencies
- Complex code contribution and automation are essential to avoid redundancy
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) are a requirement for rapid, scalable, and governed workflows
Scenarios for DAB Implementations
Consider a scenario where multiple data engineers work on a pipeline following the Medallion architecture. This pipeline involves:
- Numerous metadata files
- Redundant code spread across multiple notebooks
- Challenges in maintaining and scaling workflows
By using DABs, developers can:
- Modularize workflows by creating generic notebooks that dynamically execute with different base parameters
- Eliminate redundant code, making pipelines more scalable and maintainable
- Collaborate efficiently by packaging all necessary assets into a single bundle that can be versioned and deployed easily
CI/CD Workflow for DABs with GitLab
The following diagram represents the Databricks CI/CD pipeline using GitLab as the repository and CI/CD tool, enabling a structured and approval-based deployment process: 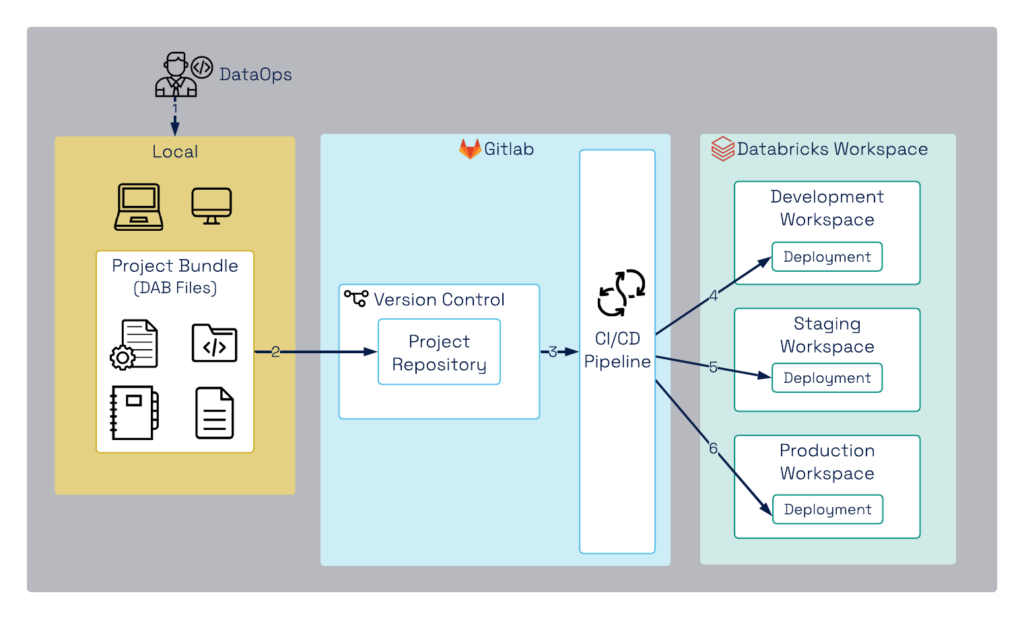
Figure 1. DAB deployment Workflow with GitLab CI/CD
- Development in Local Environment
- Developers create notebooks, job configurations, and dependencies in their local environment.
- These are packaged into a Databricks Asset Bundle (DAB), which includes:
- Notebooks
- Configurations
- Library dependencies
- Job definitions
- Version Control with GitLab Repository
- The DAB files are pushed to a GitLab repository to maintain:
- Version history for rollback and tracking
- Collaboration among teams
- Automation triggers for the CI/CD pipeline
- The DAB files are pushed to a GitLab repository to maintain:
- CI/CD Pipeline Execution with GitLab CI/CD
- Once the DAB files are committed, GitLab CI/CD triggers the pipeline, which automates:
- Code validation (linting, static analysis)
- Unit testing to verify notebook functionality
- Packaging and artifact creation
- Once the DAB files are committed, GitLab CI/CD triggers the pipeline, which automates:
- Deployment to Databricks Development Workspace
- Successfully validated DABs are deployed to the Development Workspace
- Developers test and refine their code before moving forward
- Deployment to Databricks Staging Workspace
- The CI/CD pipeline deploys the bundle to the Staging Workspace, where:
- Integration testing
- Performance testing
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT) takes place
- The CI/CD pipeline deploys the bundle to the Staging Workspace, where:
- Approval-Based Deployment to Production Workspace
- Final deployment to production requires explicit approval from:
- Management
- DataOps Leads
- Security & Compliance Teams
- Once approved, the Release Manager or an automated approval workflow in GitLab CI/CD triggers deployment to the Databricks Production Workspace. This ensures:
-
- Governance & compliance
- Risk mitigation
- Controlled and auditable releases
-
- Final deployment to production requires explicit approval from:
Advantages of Using Databricks Asset Bundles (DABs)
- Efficient Code Versioning and Collaboration
- Developers can systematically version control their code and collaborate seamlessly using GitLab repositories
- Declarative and Simple Deployment
- DABs use a simple YAML-based declarative format, allowing the deployment of multiple resources like jobs, pipelines, and Unity Catalog objects with minimal configuration
- Automated Software Development Lifecycle
- Enables organizations to apply agile methodologies and enforce a structured SDLC (Software Development Lifecycle) for Databricks projects
- Approval-Based Governance for Production Deployments
- Prevents unauthorized changes by enforcing a structured approval process before deploying to production
- Scalability & Maintainability
- Reduces code complexity by allowing reusable components and standardized configurations, making large-scale data pipelines easier to manage
In the ever-evolving world of data engineering, ensuring efficiency, scalability, and consistency across Databricks environments is essential for organizations aiming to stay competitive. By leveraging Databricks Asset Bundles (DABs) and integrating GitLab CI/CD, businesses can streamline their workflows, improve collaboration, and automate deployments, ultimately reducing operational overhead and accelerating time-to-market.
At Fresh Gravity, we understand the challenges companies face in modernizing their data infrastructure. Our team of experts is committed to helping organizations optimize their Databricks workflows through tailored solutions and industry best practices. From designing custom CI/CD pipelines to implementing governance controls and automating infrastructure provisioning, we provide end-to-end support to ensure your Databricks environment operates at its highest potential.
Reference:
1. https://docs.databricks.com/en/dev-tools/bundles/index.html
.png)